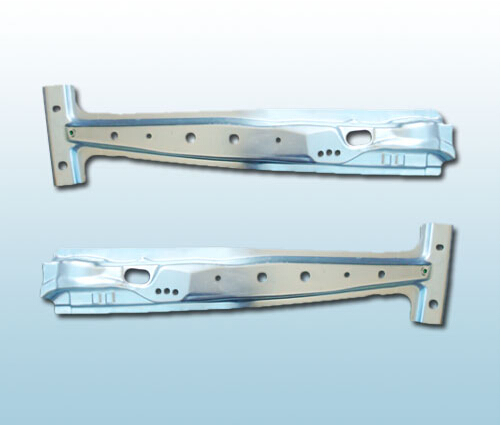

1. Design: The process starts with designing the mold based on the specifications of the product or part to be manufactured. This involves CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create precise digital models.
2. Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the mold is crucial, as it needs to withstand the manufacturing process and produce consistent results. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and alloys.
3. Machining: Once the design is finalized, the mold is machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines or other precision tools. This step involves cutting and shaping the chosen material according to the design specifications.
4. Heat Treatment: Some molds may undergo heat treatment processes to improve their hardness, strength, and durability, depending on the material used and the requirements of the molding process
5. Assembly: If the mold consists of multiple parts, they are assembled together to form the complete mold structure.
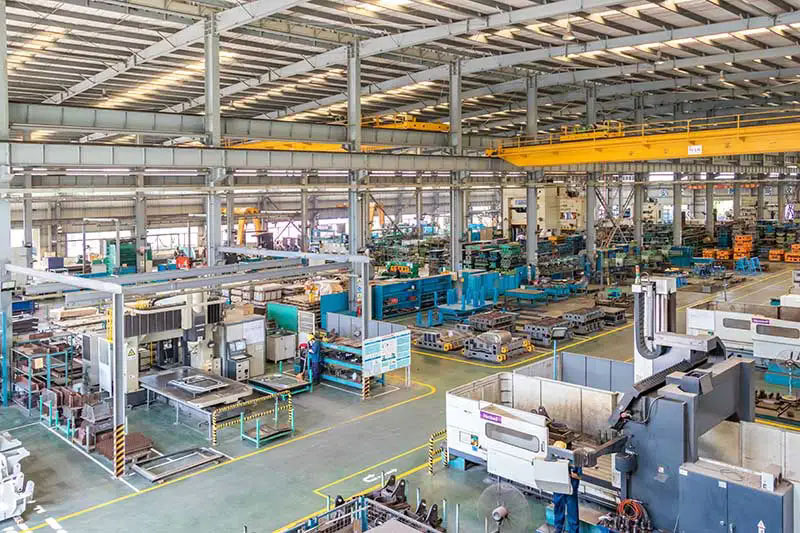

6. Finishing: Surface finishing may be applied to the mold to ensure smoothness and precision, which is critical for the quality of the final molded parts.
7. Testing and Inspection: The finished mold undergoes testing and inspection to verify its dimensions, functionality, and durability. This step ensures that the mold meets the required standards and specifications.
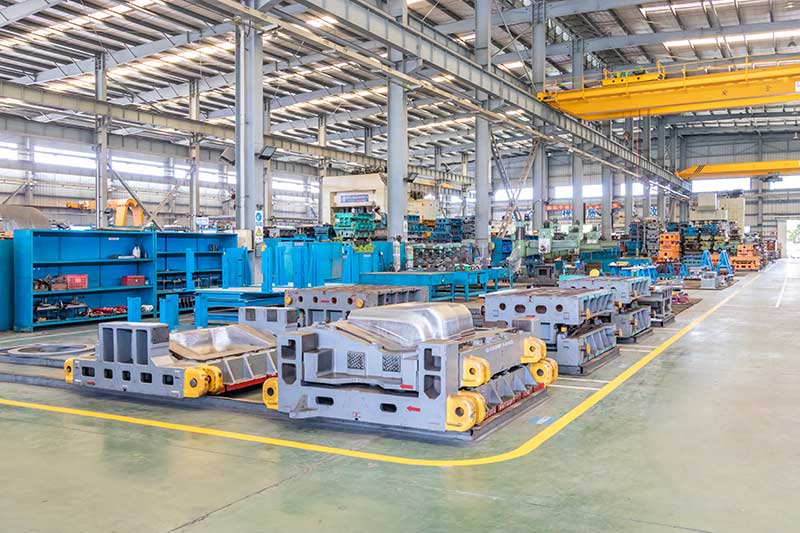

8. Production: Once the mold passes inspection, it is ready for use in production. The mold is installed in the appropriate manufacturing equipment (e.g., injection molding machine) to produce the desired parts or products in large quantities.
9. Maintenance: Regular maintenance and cleaning of molds are essential to ensure their longevity and consistent performance over time.

